Make or Buy Decision Approach: Economic Analysis
Economic Analysis
The
following inventory models are considered to illustrate this concept:
- · Purchase model
- · Manufacturing model
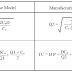
The
formulae for EOQ and total cost (TC) for each model are given in the following
table:
Where,
D = Demand per year
P = Purchase price per unit
Cc = Carrying cost per unit per year
Co = Ordering cost per order or set-up
cost per set-up
k = Production rate (No. of units per year)
r = Demand per year
Q1 = Economic order size
Q2 = Economic production size
TC = Total cost per year
Example problem for
economic analysis
An
item has a yearly demand of 2,000 units. The different costs in respect of make
and buy are as follows. Determine the best option.
Buy
|
Make
|
|
Item
cost per unit
|
Rs.
8
|
Rs.5
|
Procurement
cost per order
|
Rs.
120
|
|
Set
up cost per set up
|
Rs.
60
|
|
Annual
carrying cost per item per year
|
Rs.1.60
|
Rs.
1.00
|
Production
rate per year
|
8000
units
|
Given data
D = 2,000 units per year
For purchase model
P = Rs. 8
Co = Rs. 120 per order
Cc = Rs. 1.60 per unit per year
For manufacturing model
P = Rs. 5
Co = Rs. 60 per set-up
r = 2,000 units per year
Cc = Re 1 per unit per year
k = 8,000 units per year
Formula used
For purchase model

For manufacturing model
Solution
For purchase model
Q1 =
√ [(2 * Co * D) / Cc]
Q1 =
√ [(2 * 120 * 2000) / 1.60]
= 548 units
TC =
(D*P) + (D*Co)/Q1 + (Q1* Cc)/2
TC =
(2000*8) + (2000*120)/548 + (548*1.60)/2
= Rs. 16,876.36
For manufacturing model
Q2 =
√ [(2 * Co * r) / Cc (1-{r/k})]
Q2 =
√ [(2 * 60 * 2000) / (1.00*{1-(2000/8000)}]
=
566 units
TC =
(D*P) + (D*Co)/Q2 + Cc*(k-r)*(Q2/2k)
TC =
(2000*5) + ((2000*60)/566) + 1.0*(8000-2000)*(566/2*8000)
= Rs. 10,424.26
Decision
The cost of making is less
than the cost of purchasing. Therefore, the firm should go in for the making
option.