Present worth method
PRESENT WORTH METHOD
In this method of comparison, the cash
flows of each alternative will be reduced to time zero by assuming an interest
rate i.
Among the different alternative the best
alternative is selected based on the value of the present worth of different alternatives.
In a revenue/profit-dominated cash flow
diagram, the profit, revenue, salvage value (all inflows to an organization)
will be assigned with positive sign. The costs (outflows) will be assigned with
negative sign.
In a cost dominated cash flow diagram,
the costs (outflows) will be assigned with positive sign and the profit,
revenue, salvage value (all inflows), etc. will be assigned with negative sign.
Revenue-Dominated Cash Flow Diagram
The profit/revenue, salvage value of all
inflows to an organization will be assigned with positive sign and the cost
outflows will be assigned with negative sign is called revenue dominated cash
flow.
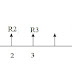
A generalized revenue-dominated cash flow
diagram to demonstrate the present worth method of comparison is presented in
Fig.
 |
| Revenue dominated cash flow diagram |
Here,
P
= Initial investment
Rj
= Revenue at the end of the ‘j’th year
i
= Interest rate compounded annually
S
= Salvage value at the end of ‘n’th year
The
present worth amount of the above revenue dominated cash flow diagram for a
given interest rate i is
PW(i) = -P + R1[1/(1 + i)1]
+ R2[1/(1 + i)2] + ... + Rj[1/(1 + i) j] + Rn[1/(1 + i)n]
+ S[1/(1 + i)n]
The above equation can be simplified
as,
PW(i) = -P + R1 (P/F, i, 1) + R2
(P/F, i, 2) + . . . + Rj (P/F, i, J) + Rn (P/F, i, n) + S (P/F, i, n)
Incase if revenue is equal for all the
given years (R1 = R2 = … = Rj = Rn = A) then the above formula is rewritten as,
PW(i) = -P + A (P/A, i, n) + S
(P/F, i, n)
The corresponding present worth amount of different
alternatives are calculated and compared. The alternative which has maximum
present worth amount should be selected as the best alternative.
Cost-Dominated Cash Flow
Diagram
The cost outflows of an organization will
be assigned with positive sign and the profit/revenue, salvage value of all
inflows to an organization will be assigned with negative sign is called cost
dominated cash flow.
A generalized cost - dominated cash flow
diagram to demonstrate the present worth method of comparison is presented in
Fig.
 |
| Cost dominated cash flow diagram |
Here,
P
= Initial investment
Cj
= Revenue at the end of the ‘j’th year
i
= Interest rate compounded annually
S
= Salvage value at the end of ‘n’th year
The
present worth amount of the above cash flow diagram for a given interest rate i
is
PW(i)
= P + C1[1/(1 + i)1] + C2[1/(1 + i)2] + ... + Cj[1/(1 +
i) j] + Cn[1/(1 + i)n] – S[1/(1 + i)n]
The above equation can be simplified
as,
PW(i) = P + C1 (P/F, i, 1) + C2
(P/F, i, 2) + . . . + Cj (P/F, i, J) + Cn (P/F, i, n) - S (P/F, i, n)
Incase if the cost is equal for all the
given years (C1 = C2 = … = Cj = Cn = A) then the above equation is rewritten
as,
PW(i) = P + A (P/A, i, n) - S
(P/F, i, n)
The corresponding present worth amount of different
alternatives are calculated and compared. The alternative which has minimum
present worth amount should be selected as the best alternative.