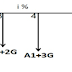
Uniform Gradient Series Annual Equivalent Method
Uniform Gradient series annual equivalent method
The objective of this mode of investment is
to find the annual equivalent amount of a series with an amount A1 at the end
of the first year and with an equal increment (G) at the end of each of the
following n – 1 years with an interest rate I compounded annually.
The corresponding cash flow diagram is shown
in Fig
Cash flow diagram of uniform gradient series annual equivalent amount
The formula to compute A under this situation
is
A = [A1
+ G {(1 + i)n – in -1}] / (1 + i)n – i = A1 + G (A/G, i,
n)
Where
(A/G, i,
n) is called uniform gradient series factor.
Example problem on uniform gradient series annual equivalent method
A person would like to invest Rs 2,500/- at
the end of the first year and thereafter he wishes to deposit the amount with
an annual increase of Rs 500/- for the following 14 years with an interest rate
of 8%. Find the total amount at the end of the 15th year of the above series.
Given data
A1 = Rs.
2,500
G = Rs.
500
n = 15
years
i = 8%
To find
F, A
Formula used
F = A
(F/A, i, n)
A = A1 +
G (A/G, i, n)
Solution
A = A1 + G (A/G, i, n)
=
2,500 + 500 (A/G, 8%, 15)
=
2,500 + 500 * 5.5945
A = Rs. 5,297.25
The future sum of the “Rs. 5,297.25” at the
end of the 15 years is,
F = A (F/A, i, n)
= 5,297.25
(F/A, 8%, 15)
= 5,297.25
* 27.152
F = Rs. 1,43,830.932
Result
The total amount received
by a person who invest Rs 2500/- at the end of the first year and deposit the
amount with an annual increase of Rs 500/- for the following 14 years with an
interest rate of 8% is Rs. 1,43,830.932 at the end of the 15th year.