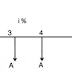
Equal-Payment Series Compound Amount Method
Equal-Payment Series Compound Amount
In
this type of investment mode, the objective is to find the future worth of n
equal payments which are made at the end of every interest period till the end
of the nth interest period at an interest rate of i compounded at the end of
each interest period. The corresponding cash flow diagram is shown in fig.
Cash flow diagram of equal-payment series compound amount
Here,
A = equal amount to be deposited at the end
of each interest period
n = No. of interest periods
i = rate of interest
F = single future amount at the end of the
nth period
The formula to obtain the present worth is
F = [A (1
+ i)n – 1] / i
= A (F/A, i, n)
Where
(F/A, i,
n) is termed as equal-payment series compound amount factor.
Example problem on equal-payment series compound amount
A person who is now 40 years old is planning
for his retired life. He plans to invest an equal sum of Rs. 7,500 at the end
of every year for the next 20 years starting from the end of the next year. The
bank gives 15% interest rate, compounded annually. Find the maturity value of
his account when he is 60 years old.
Given data
A = Rs.
7,500
n = 20
years
i = 15%
To find
F
Formula used
F = A (F/A,
i, n)
Solution
F = A (F/A, i, n)
= 7,500 (F/A, 15%, 20)
= 7,500 * 102.444
F = Rs. 7,68,330
Result
The maturity value is
Rs. 7,68,330 in his account at 15% interest rate after 20 years.